[코딩테스트 일지 - 99클럽] 9일차 - Reverse Odd Levels of Binary Tree
코딩 테스트 준비 일지 9 일차
응시 사이트 : LeetCode
난이도 : 중상
풀이시간 : 01 h 51 m
Given the root of a perfect binary tree, reverse the node values at each odd level of the tree.
For example, suppose the node values at level 3 are
[2,1,3,4,7,11,29,18], then it should become[18,29,11,7,4,3,1,2].
Return the root of the reversed tree.
A binary tree is perfect if all parent nodes have two children and all leaves are on the same level.
The level of a node is the number of edges along the path between it and the root node.
Example 1:
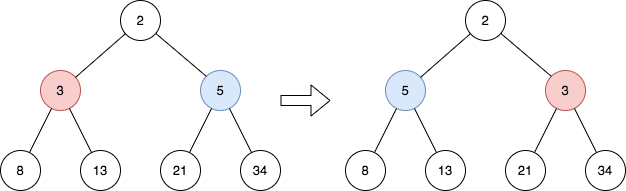
Input: root = [2,3,5,8,13,21,34]
Output: [2,5,3,8,13,21,34]
Explanation:
The tree has only one odd level.
The nodes at level 1 are 3, 5 respectively, which are reversed and become 5, 3.
Example 2:
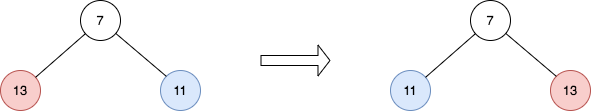
Input: root = [7,13,11]
Output: [7,11,13]
Explanation:
The nodes at level 1 are 13, 11, which are reversed and become 11, 13.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,2,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2]
Output: [0,2,1,0,0,0,0,2,2,2,2,1,1,1,1]
Explanation:
The odd levels have non-zero values.
The nodes at level 1 were 1, 2, and are 2, 1 after the reversal.
The nodes at level 3 were 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, and are 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1 after the reversal.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 214].0 <= Node.val <= 105rootis a perfect binary tree.
문제 풀이 접근
이 문제를 접했을 때, 바로 생각난 방식은 DFS 재귀 순회였고, depth % 2 == 0 일때, left, right 의 노드를 스위칭 하는 방식으로 생각해서 코드 구현을 작업했다.
결론으로 말하자면 이 문제는 dfs, bfs 모두 사용해도 상관없으며, 심지어 reverse 돌리는 것도 따로 저장해서 bfs 두번 돌리면서 역순 정렬해도 무방한 문제다. (유투브에 있는 대부분의 풀이 동영상이 이런 방식을 채택하고 있다. )
이 문제를 풀면서 단순히 왼, 오의 값을 변경하는데 초점을 맞춰버려서 시간을 오래걸리고 제대로 된 구현을 하는것이 힘들었다.
결국 다른 사람의 풀이를 보면서 어떻게 풀어야 깔끔하고 빠르게 풀지를 체크해 보았는데, 이미 문제에서 힌트는 전부 주어지고 있었다. 완벽한 2진 트리를 준다는 것. 결국 여기서 알 수 있는 정보는 왼쪽 끝단, 오른쪽 끝단 이 둘은 서로 매칭되며, 왼쪽 끝의 오른쪽 노드와 오른쪽 끝의 왼쪽노드도 매칭된다.
결국, 모든 노드는 매칭이 된다는 것이다.
플로우는 아래와 같다.
1. Left는 Left 쪽으로 계속 뻗어나간다.
2. 마찬가지로 Right는 Right 쪽으로 계속 뻗어나간다.
3. 이후 그 다음 왼쪽 끝에서 오른쪽 노드, 오른쪽 끝에서 왼쪽노드 처럼 안쪽으로 조여가며 매칭된 것을 뒤집어 준다.
정답 작성 코드 ( C# )
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode ReverseOddLevels(TreeNode root) {
DFS(ref root.left,ref root.right, true);
return root;
}
public void DFS(ref TreeNode rootLeft, ref TreeNode rootRight, bool isOdd)
{
if(rootLeft == null)
return;
if(isOdd == true)
{
int temp = rootLeft.val;
rootLeft.val = rootRight.val;
rootRight.val = temp;
}
DFS(ref rootLeft.left, ref rootRight.right,!isOdd);
DFS(ref rootLeft.right,ref rootRight.left, !isOdd);
}
}코드 결과
