[코딩테스트 일지 - 99클럽] 8일차 - Evaluate Boolean Binary Tree
코딩 테스트 준비 일지 8 일차
응시 사이트 : LeetCode
난이도 : 중하
You are given the root of a full binary tree with the following properties:
Leaf nodes have either the value
0or1, where0representsFalseand1representsTrue.Non-leaf nodes have either the value
2or3, where2represents the booleanORand3represents the booleanAND.
The evaluation of a node is as follows:
If the node is a leaf node, the evaluation is the value of the node, i.e.
TrueorFalse.Otherwise, evaluate the node's two children and apply the boolean operation of its value with the children's evaluations.
Return the boolean result of evaluating the root node.
A full binary tree is a binary tree where each node has either 0 or 2 children.
A leaf node is a node that has zero children.
Example 1:
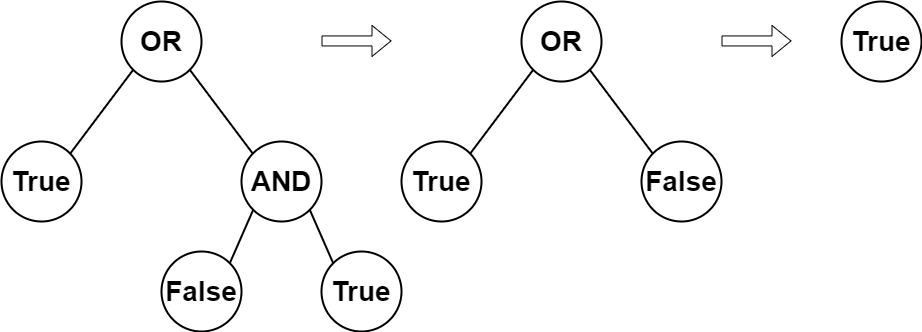
Input: root = [2,1,3,null,null,0,1]
Output: true
Explanation: The above diagram illustrates the evaluation process.
The AND node evaluates to False AND True = False.
The OR node evaluates to True OR False = True.
The root node evaluates to True, so we return true.Example 2:
Input: root = [0]
Output: false
Explanation: The root node is a leaf node and it evaluates to false, so we return false.
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000].0 <= Node.val <= 3Every node has either
0or2children.Leaf nodes have a value of
0or1.Non-leaf nodes have a value of
2or3.
문제 풀이 접근
이 문제는 단순 경로 탐색처럼 진행하면 되는 문제처럼 보였는데, 탐색 이후 처리가 더 중요했던 문제였다.
이 문제를 봤을때, 딱 해결 방법이 DFS로 하는것이 좋아보여서, DFS 말고 다른 방법은 고려하지 않았다.
딱 문제의 생김새가 부모의 Root 노드가 0,1 이 아니고 2,3 이면서 left, right 가 null 일때를 참고해서 계산한 후에 내 root 의 value 값을 갱신하면 되는것 처럼 생겼다.
다행히 풀이 방법이 틀리지 않아서 문제를 용이하게 풀었으나, 중간에 조금 해맸다.
받은 데이터의 value는 어차피 중요하지 않아서 덮어씌워도 됐었는데, stack 으로 탐색한 경로를 수집하다가 나중에 다 수집하고나서 결과를 연산하는 방식으로 하니까 아무래도 연산하는 순서나 이런 부분에서 꼬이는 것이 많이 있었다. 그래서 이 방법은 시원하게 폐기하고 stack 지워버리고 재귀로 해결했다.
문제를 푸는 플로우는 다음과 같다.
1. DFS를 만들고, 바로 left, right 순으로 순회시킨다. 예외 처리로는 left,right 가 모두 null 인 경우로 처리한다.
2. 이후 left, right 순으로 순회한 다음 root.value 가 2,3 인 경우 OR, AND 의 경우 값만 처리해주고 결과를 bool 값으로 리턴한다.
3. 추가로 첫 입력 데이터 root 가 0, 1 으로 하나만 들어오는 경우의 값도 처리하여 종료해준다. ( 이때는 바로 root.Value 를 Convert.ToBoolean()으로 변수를 컨버팅해서 반환하면 된다)
정답 작성 코드 ( C# )
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution
{
public bool EvaluateTree(TreeNode root)
{
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return Convert.ToBoolean(root.val);
bool dd = DFS(root);
return dd;
}
public bool DFS(TreeNode root)
{
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return false;
DFS(root.left);
DFS(root.right);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return false;
switch(root.val)
{
case 2:
root.val = (root.left.val == 0 && root.right.val == 0) ? 0 : 1;
break;
case 3:
root.val = (root.left.val == 1 && root.right.val == 1) ? 1 : 0;
break;
}
return Convert.ToBoolean(root.val);
}
}코드 결과

프로젝트에서 바로 돌릴 수 있는 코드 ( C# )
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.ComponentModel.Design;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Security.AccessControl;
using System.Security.Authentication;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Web;
using System.Xml.Linq;
using static CodingTestProj.Program;
namespace CodingTestProj
{
public class TreeNode
{
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val = 0, TreeNode left = null, TreeNode right = null)
{
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
/* Condition
* 1 . FULL BT
*
*
*
*
*/
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode(0);
TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode(0);
TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode node7 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode node8 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode node9 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode node10 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode node11 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode node12 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode node13 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode node14 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode node15 = new TreeNode(1);
node1.left = node2;
node1.right = node3;
node2.left = node4;
node2.right = node5;
node3.left = node6;
node3.right = node7;
// 4 , 5 X
node6.left = node8;
node6.right = node9;
node7.left = node10;
node7.right = node11;
node9.left = node12;
node9.right = node13;
node12.left = node14;
node12.right = node15;
Solution solution = new Solution();
solution.EvaluateTree(node1);
}
}
public class Solution
{
public bool EvaluateTree(TreeNode root)
{
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return Convert.ToBoolean(root.val);
bool dd = DFS(root);
return dd;
}
public bool DFS(TreeNode root)
{
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return false;
DFS(root.left);
DFS(root.right);
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return false;
switch(root.val)
{
case 2:
root.val = (root.left.val == 0 && root.right.val == 0) ? 0 : 1;
break;
case 3:
root.val = (root.left.val == 1 && root.right.val == 1) ? 1 : 0;
break;
}
return Convert.ToBoolean(root.val);
}
}
}